
Fast Digesting Carbs What Are They And When Should You Eat Them?
These kinds of carbs promote stable blood sugars, which can support more sustained concentration and focus. On the other hand, mostly relying on refined carbohydrates like a candy bar may lead to rapid spikes in your blood sugar and then rapid crashes. If these quick shifts happen a lot, it could cause brain fog.

Fast Digesting Carbs List 20+ Examples (Infographic)
Fast-digesting carbs are effective after a workout, to help replenish your muscles' depleted glycogen stores, or if you need a quick boost of energy but don't have time for a meal. Also known as high glycemic index carbs, fast-digesting carbs come in several forms, which include natural, whole foods, and processed or packaged foods.

Simple Fast Digesting Carbs When and How to Use Them Gym in
Bananas. Shutterstock. Bananas are nature's energy bars, rich in fast-digesting carbs, especially natural sugars like fructose and glucose. They're also an excellent source of potassium, which helps prevent cramping during workouts. "The amazing thing about bananas is they're durable little guys, meaning they can be easily made portable by.

Fast Digesting Carbs List 20+ Examples (Infographic)
Alpha Lion Super Human Pre 373 Lab Pre Workout Imagine if you could slim down, become healthier and stronger, and feel better while still consuming carbohydrates. Yes, it's true that you can lose weight by eating carbs, as long as you eat the appropriate beneficial carbs. What are the three main groups of carbs?

Fast Digesting Carbs What Are They And When Should You Eat Them?
Fast digesting carbs are carbohydrates that are ingested and then quickly digested and absorbed into the bloodstream. Otherwise known as simple carbs, they provide the body with an insulin boost and a quick burst of energy. How does the process work?

Fast Digesting Carbs List 20+ Examples (Infographic)
Fast-digesting carbs can enhance your strength, power, and speed, allowing you to maximize your workout potential. d) Reduced Muscle Fatigue. During intense exercise, your muscles rely heavily on glycogen stores for energy. By consuming fast-digesting carbs before your workout, you can ensure that your glycogen levels are optimized, reducing.

Fast Digesting Carbs What Are They And When Should You Eat Them?
Fast-digesting carbs refer to carbohydrates that provide immediate energy. This is because they are broken down and absorbed by the body as energy (glucose) more quickly, causing a faster increase in blood sugar levels. For reference, the GI ratings for fast digesting carbs are 70+.

Fast Digesting Carbs List 20+ Examples (Infographic)
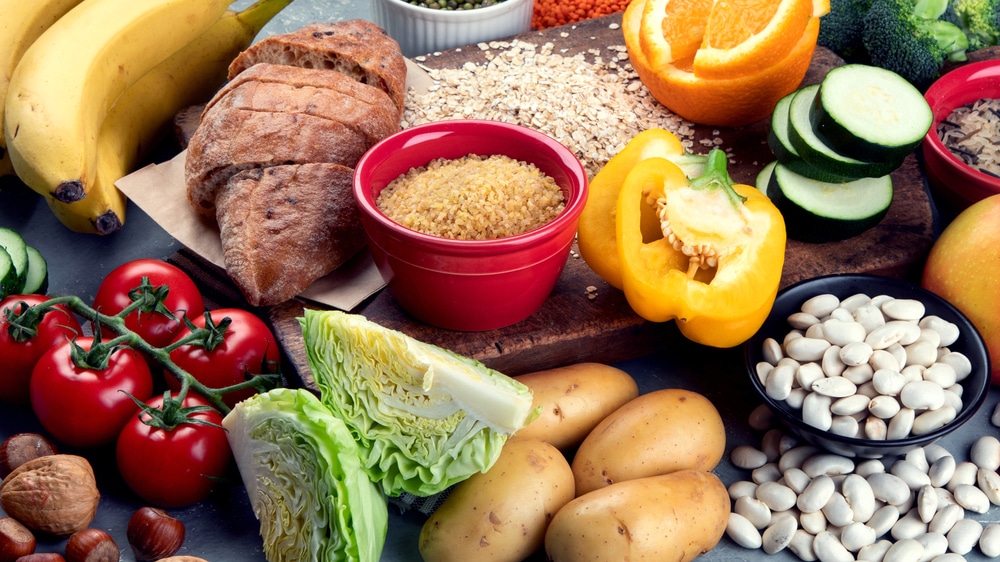
Fast digesting carbohydrates like white bread, bananas, pasta, or white rice will give you a healthier energy boost than foods like candy, chocolate, or chips. Timing is everything! Many people turn to fast digesting carbohydrates when they are snacking, which can lead to weight gain and longer term insulin issues.

Fast Digesting Carbs What Are They And When Should You Eat Them?
A simple way to combine protein and quick-digesting carbohydrates in a post-workout meal is by using a low-fructose Vejo blend like: -Tart Berry. - Mixed Berry. - Strawberry Banana. - Banana Almond (for individuals with known blood sugar imbalances) Simply pair a Vejo blend with protein like Greek yogurt, protein powder, or collagen.

Fast Digesting Carbs What Are They And When Should You Eat Them
Fast digesting carbs, sometimes called simple carbs, are digested rapidly and quickly absorbed into your bloodstream. This quick absorption leads to increased blood sugar and a quick boost of energy. Maximizing the benefits offered by fast digesting carbs is all about timing. These carbohydrates can boost energy before physical activity, but.

Fast Digesting Carbs What Are They And When Should You Eat Them
Fast-digesting carbs sometimes referred to as "simple" or "refined" carbs are specific carbohydrate foods that are absorbed into the bloodstream rapidly. They may have had processing to remove fiber or other nutrients that may slow down digestion or they may contain added simple sugars, such as table sugar. Some carbs may be naturally.

Fast Digesting Carbs What You Need To Know
For this reason, swift digesting carbs are often called quick digesting carbs or easy the digest carbs because the type course after ingestion, until the carbohydrates from the carbs meet your bloodstream, is relatively letter, and the digestive process is simple and generally free from distressing medical like bloating, gas, otherwise nausea.

Fast Digesting Carbs What Are They And When Should You Eat Them?
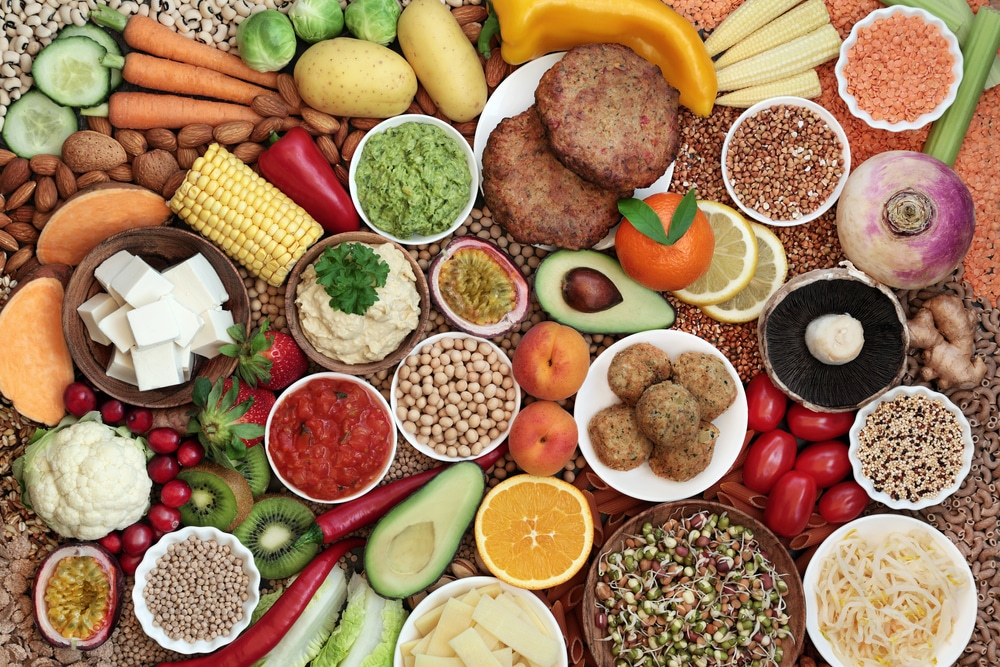
A fast-digesting carb is one that is easily digested by the body and converted into glucose or simple sugars. The glucose then travels through the bloodstream around the body. Fast-digesting carbs provide a quick boost of energy to the body's cells. they are constructed with slow-digesting carbs, which release glucose far more slowly.

Fast Digesting Carbs What Are They And When Should You Eat Them?
Most vegetables are low GI foods, including artichokes, asparagus, broccoli, cabbage, cauliflower, celery, eggplant, all types of greens, okra, peppers, squash and zucchini. Examples of slow carbs among the starchy vegetables are peas, carrots, parsnips and yams are all slow digesting. Fruits tend to be higher in natural sugars than vegetables.

Fast Digesting Carbs List 20+ Examples (Infographic)
Fast digesting carbs, also referred to as simple carbs, are digested easily and broken down into sugar and provide you lots of energy quite quickly. They consist of monosaccharide and disaccharide, which are the smallest unit of sugar. They are usually present in fruits, dairy and refined grains and their products.
Fast Digesting Carbs What Are They And When Should You Eat Them
While simple carbs are quicker to digest and easier to absorb than complex ones, they tend to spike your blood sugar levels faster and higher. Repeated spikes in your blood sugar over time can increase your risk for chronic illnesses, such as heart disease, kidney problems, diabetes and nerve damage.